User Task
Introduction
A User Task is a typical “workflow” Task where a human performer performs the Task with the assistance of a software application and is scheduled through a task list manager of some sort.
— BPMN 2.0.2 Standard, 10.3.3, User Task
In Flowable, User Tasks are the primary way to interact with humans within a process. Once the execution reaches such a task, a user is required to fill in a form of some sort.
Through forms, it is possible to create and update variables which can be used in other tasks or can be used to control the flow of a process.
Each task can be assigned to one or more people as well as shared with any number of groups. In addition, a task can optionally have a due date.
Example
The following example shows how a process where a user is required to fill a form. The information gathered is used to create an invoice.
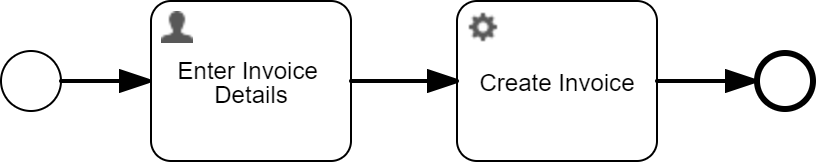
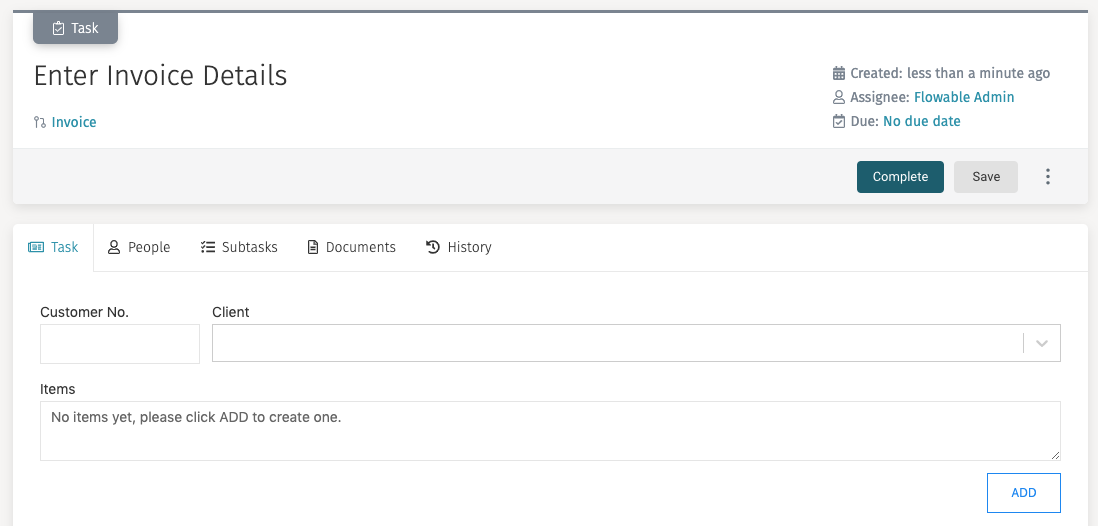
A simple corresponding form could look like this:
Properties
General
Common
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model Id | Text | Model Id identifies the element within the process model. | |
| Name | Text | The name of the element. This is the name displayed in the diagram. | |
| Documentation | Multiline Text | A free-form text that can be used to explain details about the particular element. | |
| Due date | Date | Due date of the task. It can either be an be an absolute value, a value relative to the creation date or an expression. | |
| Priority | Text | The priority can be be used to sort or categorize tasks. Defaults to priority 50 if left empty. | |
| Category | Text | Category of User Task. This allows you to group user tasks by your own criteria. |
Form
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form reference | Reference | Reference to the form that will be displayed when opening this task. | |
| In same deployment | Boolean | Set it to true if the referenced definition should be referenced from within the same app deployment. Set it to false to always use the newest definition. |
SLA
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA reference | Reference | Reference to the SLA that will be used |
Assignment
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assignee | User Selection | User ID of the task's assignee. The assignee can see and complete a task and is usually the person responsible for it. | |
| Owner | User Selection | The ID of the task's owner. | |
| Candidate users | User Selection | By selecting one or more candidate users, the task might be taken by one of those users. If the task is not specifically assigned to one of the users directly, it will show up in all of the selected candidate users tasks list until assigned directly. | |
| Task candidates type | Selection:
| Defines the filter on the list of users when changing the assignee of a task. | |
| Candidate groups | Group Selection | By selecting one or more groups as the candidate groups, shares the task with all users belonging to at least one of the groups. If there is no specific assignee specified but the task has candidate groups, the task will show up in all users task list belonging to at least one of the groups until the task is assigned to a specific user. | |
| Watcher users | User Selection | The selected users will be added as watcher identity links to the task. | |
| Watcher groups | Group Selection | The selected groups will be added as watcher identity links to the task. | |
| Participant users | User Selection | The selected users will be added as participant identity links to the task. | |
| Participant groups | Group Selection | The selected groups will be added as participant identity links to the task. | |
| Disallowed users for assignee | User Selection | When set, any of these users will be disallowed from being an assignee for this user task. | |
| Disallowed groups for assignee | Group Selection | When set, a user of any these groups will be disallowed from being an assignee for this user task. | |
| Disallowed task completers for assignee | TaskSelect | When set, any user that has completed a referenced task will be disallowed from being an assignee for this user task. |
Multi Instance
Multi instance
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi instance type | Selection:
| The type of multi-instance: default is 'None' meaning a single instance is created at runtime. Select either 'Parallel' or 'Sequential' if you want multiple instances to be created. | |
| Collection | Text | References a collection variable (for example a JSON array variable) by its name or using an expression that resolves to a collection. | |
| Element variable | Text | The name of the variable where the currently processed element from the multi-instance collection configured above will be stored (for example, 'invoicePosition'). The element can then be accessed through an expression, e.g., ${invoicePosition}. | |
| Element index variable | Text | The name of the variable where the index of the currently processed item from the multi-instance collection will be stored, for example, 'itemIndex'. The index is a number starting with 0 which is increased with every element that is being created. The index can then be accessed through an expression, e.g., ${itemIndex} further on in the process. | |
| Cardinality | Text | A fixed number or an expression that resolved to an integer that controls the number of instances that will be created. This is typically used when there is no collection available or needed. | |
| Completion condition | Text | An expression that should resolve to a boolean value. When evaluating to true, the remaining activity instances will be removed and the process instance will continue. |
Variable aggregation
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Aggregations | List | Define an aggregation. Each element in this list will result in one aggregation variable. |
Advanced
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optimize for only automatic steps | Boolean | (Advanced setting, only check it if you understand the implications) If checked, this instructs the Flowable engine that the multi-instance only contains automatic tasks and no wait states. In this situation, an asynchronous job is created when the multi-instance activity is entered that keeps checking if all instances are completed and completes the multi-instance. The benefit of this approach is that it is light on resources versus alternatives and doesn't lead to optimistic locking exceptions. |
Advanced Form
Data mapping
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input mapping type | Selection:
| Defines the type for the mapping definitions, which can be allowed or blocked. | |
| Input mappings to form | List | Defines the input mappings that are allowed or blocked for the task form. | |
| Output mapping type | Selection:
| Defines the type for the mapping definitions, which can be allowed or blocked. | |
| Output mappings to form | List | Defines the output mappings that are allowed or blocked for the task form. |
Validation
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Validate form fields (server-side) | Boolean | If the form is submitted and validate form fields expression evaluates to true, form fields are validated on the BE side according to the form model restrictions. |
Legacy
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form properties | List | Custom form properties which are used within the legacy Flowable form engine or a custom form engine. |
Security
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security policy | Reference | Allows to set a custom security policy. |
UI Configuration
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expose to case view | Boolean | Should this task be exposed at runtime in the case view. | |
| Label | Text | Define a label for the runtime display of this element | |
| Icon | Icon | Choose an icon for the runtime display of this element | |
| Index | Text | Define an index for the ordering in the runtime display of this element | |
| Active | Selection:
| Define how the element should be rendered in a state of Active | |
| Completed | Selection:
| Define how the element should be rendered in a state of Completed | |
| Header configuration | Selection:
| Choose a header configuration or fill-in a custom header config value. |
Advanced
Execution
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skip expression | Text | If the Skip expression evaluates to true, the flow is taken regardless of any condition. It is required to opt-in to this feature by setting a variable _FLOWABLE_SKIP_EXPRESSION_ENABLED with the Boolean value true on the process instance. | |
| Include in history | Boolean | When the history level is set to "instance" or "task" level with this property it can be configured if this activity instance should be included in the historic activity data. | |
| Task ID variable | Text | An optional variable that holds the ID of the created task instance. | |
| Is for compensation | Boolean | Determines whether the activity can serve as a compensation for another activity. | |
| Asynchronous | Boolean | When enabled, the activity will be started as an asynchronous job. The process state is persisted before this element is executed. Then, the process execution will be resumed asynchroneously. This can be used when the execution an activity takes a long time to return the UI to the user quicker in case the user does not need to see the next step immediately. However, if an error occurs before the following wait state, there will be no direct user feedback. Please refer to the documentation for more details. | |
| Exclusive | Boolean | Determines whether the activity or process is run as an exclusive job. An exclusive job makes sure that no other asynchronous exclusive activities within the same process are performed at the same time. This helps to prevent failing jobs in concurrent scenarios. | |
| Leave asynchronously | Boolean | When enabled, the activity will be left as an asynchronous job. This means that the activity is ended asynchronously, including end execution listeners. Please refer to the documentation for more details. | |
| Leave exclusive | Boolean | Determines whether the activity should leave as an exclusive job. An exclusive job makes sure that no other asynchronous exclusive activities within the same process are performed at the same time. This helps to prevent failing jobs in concurrent scenarios. | |
| Job Category | Text | When set, the underlying generated job will have a Job Category, which will be executed only by Application Servers, where the Process Engine has enabledJobCategories set to this category. | |
| Task Completer variable | Text | An optional variable that holds the User ID of the completer of this task instance. |
Advanced options
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Folder path for uploaded content items | Text | Set a folder path to define the folder where uploaded content items need to be uploaded to. |
Listeners
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Execution listeners | List | Allows invoking custom after certain lifecycle events. Start: Executes after the activity has been started. End: Executes after the activity was completed. Transition: When defined on a sequence flow, executes once the flow is transition is taken. | |
| Task listeners | List | Allows you to invoke Java logic after the creation, the reassignment, the completion and the deletion of the task. |
Visual
| Attribute | Type | Description | Category |
|---|---|---|---|
| Background color | Color | The background color of the element in the diagram. | |
| Font size | Selection:
| Font size. | |
| Font weight | Selection:
| Select the style between bold and normal. | |
| Font style | Selection:
| Select the style between italic and normal. | |
| Font color | Color | Select a font color. | |
| Border color | Color | The border color of the element in the diagram. |
List Attribute Details
Variable Aggregations
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Target (Variable / Expression) | Text | The name of the target variable or an expression that gives the variable name |
| Type | Selection:
| The type of aggregation. Use 'default' to use the standard behavior of creating an aggregation JSON variable. Use 'custom' to define a delegate expression that will handle the aggregation. Please see the documentation for more information. |
| Delegate Expression | Text | Define a delegateExpression that will resolve to an instance of VariableAggregator (for BPMN) or PlanItemVariableAggregator (for CMMN). This instance will then be responsible for aggregating the variables. |
| Class | String | A class that implements VariableAggregator (for BPMN) or PlanItemVariableAggregator (for CMMN). This instance will then be responsible for aggregating the variables. |
| Target variable creation | Selection:
| Configures the way the aggregation variable is created. The 'Default' option creates the aggregation variable when all instances of the multi-instance have been completed. Use 'Create overview variable' to create a variable at the start of the multi-instance and keep it up to date during multi-instance exeution. Once all the instances are completed it will create a JSON variable in the same way as for Default target variable creation. Use the 'Store as transient variable' option to have the default behavior, but store the resulting aggregation variable transiently. |
| Variable Definitions | BasicFormList | property.loopVariableAggregation.definitions.description |
Variable Definitions
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Source (Variable / Expression) | Text | The name of the source variable or an expression that provides the value |
| Target (Variable / Expression) | Text | The name of the aggregation variable or an expression that resolves to a variable name. |
Input mappings to form
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mapping value | Text |
Output mappings to form
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mapping value | Text |
Form properties
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Text | A unique identifier for this form property. |
| Name | Text | A name for the form property. |
| Type | Selection:
| The type of the form property |
| Custom type | Text | |
| Expression | Text | An expression used to determine the value of this form property |
| Variable | Text | The variable to map the value on to. |
| Default | Text | The default value if not set (an expression). |
| Required | Boolean | |
| Readable | Boolean | |
| writable | Boolean | |
| Date pattern | Text | A java-compatible data pattern, such as dd-MMM-yyyy or yyy-MM-dd. |
| Form values | BasicFormList | |
| Form values | BasicFormList |
Form values
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Text | A unique identifier. |
| Name | Text | The name of the enum field value. |
Form values
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Id | Text | A unique identifier. |
| Name | Text | The name of the custom field value. |
Execution listeners
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Event | Selection:
| The lifecycle event. The 'Take' event is only available for sequence flow. |
| Class | Text | Fully qualified classname of a class to be invoked when executing the task. The class must implement either JavaDelegate or ActivityBehavior. |
| Expression | Text | JUEL Expression to be executed when the task is started. Expressions allow you to interact with the backend by calling services, making calculations etc. You can find more information about expressions in the documentation. |
| Delegate expression | Text | Delegate Expression to be executed when the task is started. A delegate expression must resolve to a Java object, for instance a Spring bean. The object's class must implement either JavaDelegate or ActivityBehavior. |
| Fields | List |
Fields
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Text | The name of the element. This is the name displayed in the diagram. |
| String value | Text | |
| Expression | Text | JUEL Expression to be executed when the task is started. Expressions allow you to interact with the backend by calling services, making calculations etc. You can find more information about expressions in the documentation. |
| String | Text |
Task listeners
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Event | Selection:
| The type of event that the listener should listen to. |
| Class | Text | Fully qualified classname of a class to be invoked when executing the task. The class must implement either JavaDelegate or ActivityBehavior. |
| Expression | Text | JUEL Expression to be executed when the task is started. Expressions allow you to interact with the backend by calling services, making calculations etc. You can find more information about expressions in the documentation. |
| Delegate expression | Text | Delegate Expression to be executed when the task is started. A delegate expression must resolve to a Java object, for instance a Spring bean. The object's class must implement either JavaDelegate or ActivityBehavior. |
| Fields | List |
Fields
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Text | The name of the element. This is the name displayed in the diagram. |
| String value | Text | |
| Expression | Text | JUEL Expression to be executed when the task is started. Expressions allow you to interact with the backend by calling services, making calculations etc. You can find more information about expressions in the documentation. |
| String | Text |