MCP Parameters
MCP Input Parameters
The input parameters of an MCP service model operation define the arguments that are passed to the MCP tool when it is invoked. Each input parameter maps to a named argument of the tool.
- Label: The human-readable name for the input parameter.
- Name: The technical name of the parameter, used as the argument name when calling the MCP tool.
- Type: The type of the input. Supported types are String, Integer, Long, Double, Boolean, Date, JSON, and Array.
- Description: A description of the input parameter for documentation purposes.
- Required: Whether the input parameter is required.
- Default Value: The default value to use in case the parameter has not been provided. Can be a fixed value or an expression.
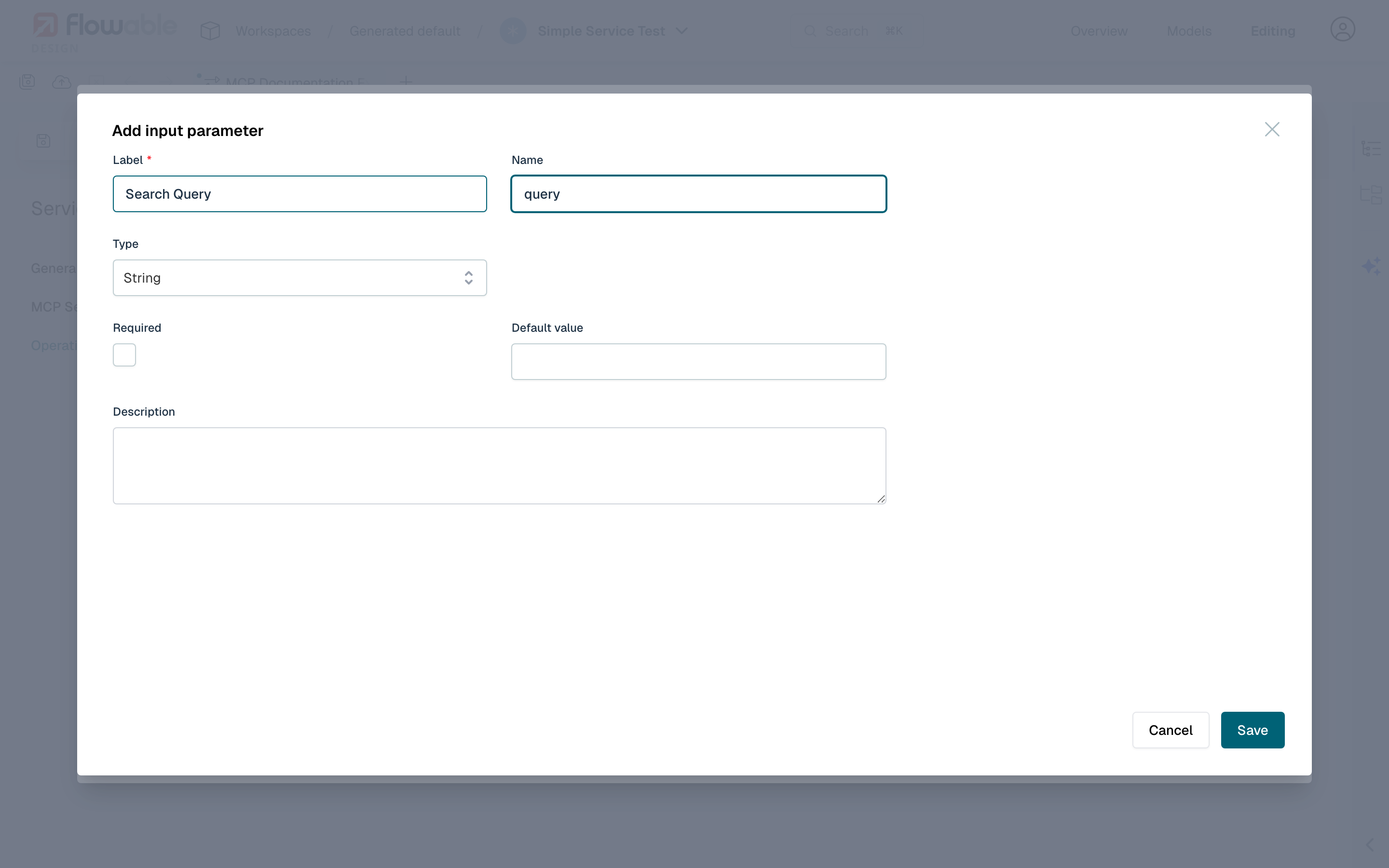
Unlike REST services, MCP input parameters do not have a Query Parameter option, as MCP tools use named arguments rather than URL query strings.
The input parameter values are automatically converted to the appropriate types when passed to the MCP tool:
- String values are passed as-is.
- Integer, Long, and Double values are converted to their numeric representations.
- Boolean values are passed as
trueorfalse. - Date values are formatted in ISO 8601 format.
- JSON and Array values are passed as structured objects.
MCP Output Parameters
The output parameters define how the response from the MCP tool is mapped back into the process or case:
- Label: The human-readable name for the parameter.
- Source: The source of the output parameter data. MCP services provide the following sources:
- Default: If the MCP tool call result contains structured content, it is used as the source of data. Otherwise, the engine falls back to the text content and automatically attempts to parse it as JSON. If the text is valid JSON, output parameters are extracted from the parsed JSON structure using their configured paths and names. If the text is not valid JSON, it is treated as a plain string value.
- Full structured content: The structured content returned by the MCP tool call (
mcpStructuredContentin JSON). This contains machine-readable structured data and is available as a JSON type. Use this when the MCP server returns structured content alongside text content. - Text content: The text content returned by the MCP tool call (
mcpTextContentin JSON). This contains the human-readable text portion of the response and is available as a String type.
- Name: The technical name of the parameter, as used at runtime by the engine logic.
- Type: The type of output parameter.
- Path: Uses JSON Pointer syntax to navigate through nested JSON structures (e.g.,
/results/0/name). - Mapping name: In situations where names overlap, a different mapping name can be given to allow the runtime to distinguish between parameters.
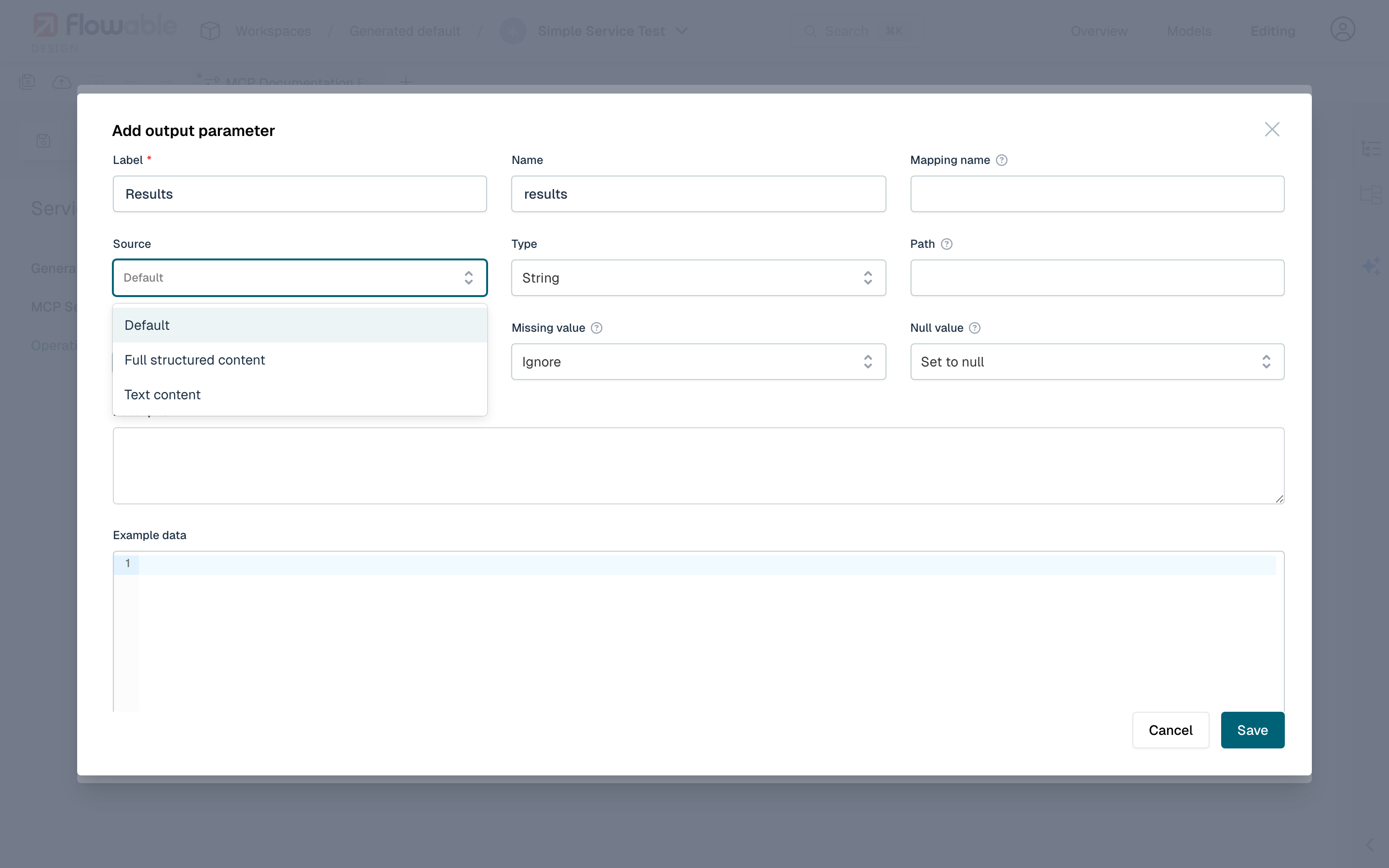
When using the Full structured content source, the structured content is always available as JSON. If the tool only returns text content (no structured content), use the Default source instead — the engine will attempt to parse the text as JSON automatically.
The following table summarizes the available output sources:
| Source | Description | Available Types |
|---|---|---|
| Default | Uses structured content if available, otherwise falls back to text content. Text is automatically parsed as JSON if possible; otherwise treated as a plain string. | String, Integer, Long, Double, Boolean, Date, JSON, Array |
| Full structured content | The structured content returned by the MCP tool call (mcpStructuredContent). Useful when the tool returns machine-readable data. | JSON |
| Text content | The text content returned by the MCP tool call (mcpTextContent). Contains the human-readable text portion of the response. | String |