Request Response Handlers
This is an old version of the documentation for Flowable until version 3.13 and for the Angular-based Flowable Design 3.14/3.15. If you are running the latest version of Flowable please check out the current version of this page.
When integrating with REST APIs using the Service Registry with Service Type set as REST,
the structure of the requests and responses may not always match the expectation of the process or case.
To address this issue, Flowable provides support for Request / Response Handlers.
These handlers can be configured using scripts or expressions to manipulate data and align it with the required request/response format.
Scripts as Request and Response Handlers
Consider an example where an API returns Customer objects in the following format:
{
"id" : "johndoe",
"firstName": "John",
"lastName": "Doe"
}
To retrieve a customer object using the Service Registry, configure a service operation with a GET API call to the Customer Service:
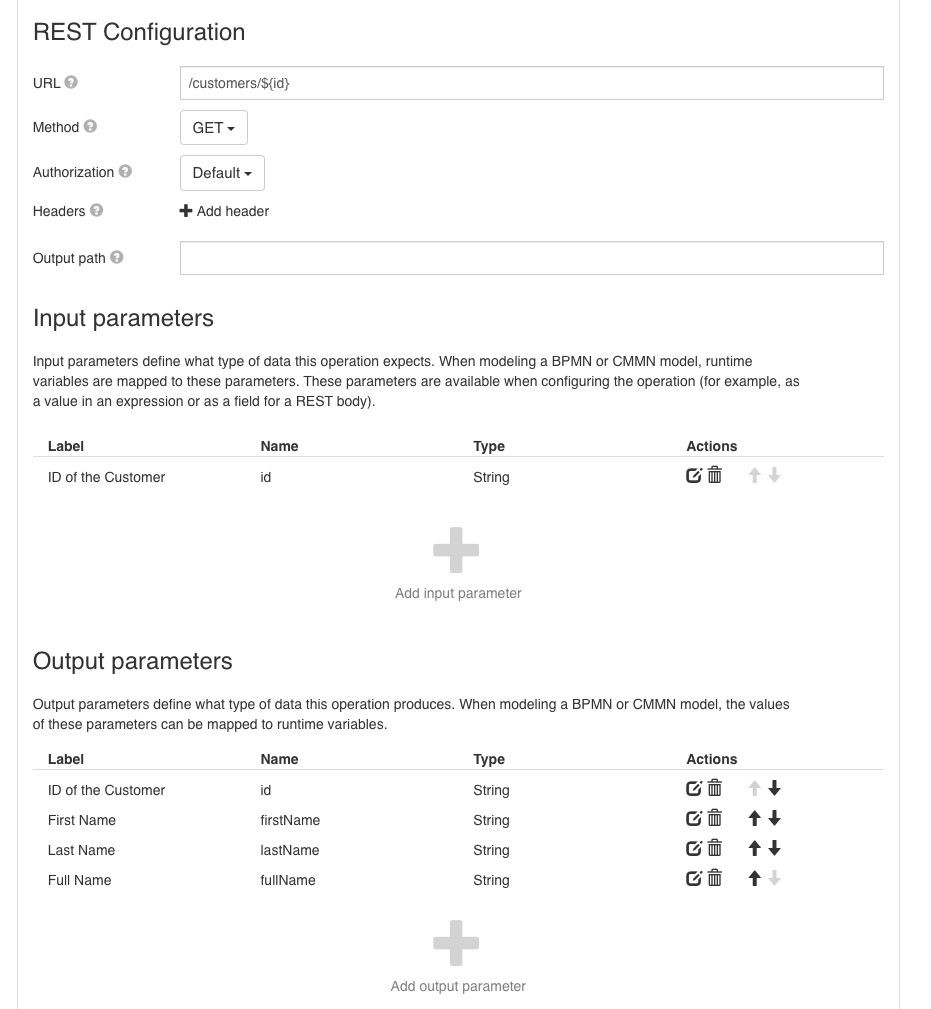
In the screenshot above, the API expects an id as input and returns the id, firstName and lastName of the customer.
However, let's assume we also require a new field called fullName, which should be calculated based on the firstName and lastName fields.
In this case, you can configure a Response handler script:
// Retrieve Response Body and transform to JSON object
var response = flw.json.stringToJson(flwHttpResponse.getBody());
// Get attributes from response body
var firstName = response.path("firstName").asString();
var lastName = response.path("lastName").asString();
// Add a new attribute to the response body
var fullName = firstName + " " + lastName;
response.putString("fullName", fullName);
// Set response body
var jsonResponse = flw.json.jsonToString(response);
flwHttpResponse.setBody(jsonResponse);
In the above example, the Response handler takes the response, transforms it to a JSON object, calculates the fullName
field based on the firstName and lastName, adds it to the response, and sets the modified response body using flwHttpResponse.
The Service Registry executes the API, applies the Response handler, and parses the result for the output parameters.
Since the fullName field is now part of the response, it will be returned seamlessly as an output parameter.
Expression-based Request and Response Handlers
Instead of using a script, it is also possible to use expressions instead. This allows to execute a custom Java method.
It is not necessary to implement a specific interface, the method is executed as is and doesn't expect a specific return type.
In the expression the variables flwHttpRequest, flwHttpResponse, flwServiceOperation and flwServiceDefinitionModel are available.
An example for such an expression is:
${myCustomUtil.addFullNameToBody(flwHttpResponse)}
While the method needs then to implement the signature: void addFullNameToBody(HttpResponse httpResponse).
flwHttpRequestis an instance of the classorg.flowable.http.common.api.HttpRequestflwHttpResponseis an instance of the classorg.flowable.http.common.api.HttpResponseflwServiceOperationis an instance of the classcom.flowable.serviceregistry.api.repository.ServiceOperationflwServiceDefinitionModelis an instance of the classcom.flowable.serviceregistry.api.repository.ServiceDefinitionModel